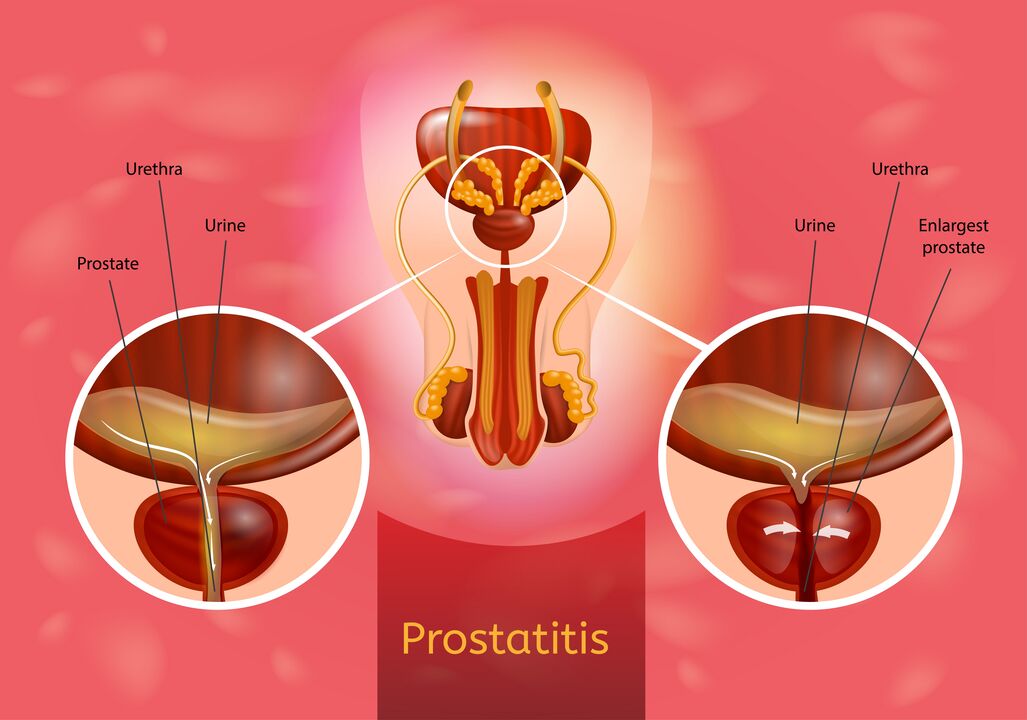
Prostatitis is a disease of prostate (prostate), developing as a result of inflammatory changes in it.According to statistics, the incidence of the disease reaches 35-50% and is detected in men aged 20-40.
Type
4 types of prostatitis are distinguished:
- acute (bacteria);
- chronic bacteria;
- not a space;
- There are no chronic symptoms.
Acute prostatitis is very rare due to the rapid process of inflammation and instant transition to the chronic phase (improvement).
Prostatitis is not chronic surgery, otherwise it is called chronic pelvic pain syndrome, which can be inflamed (with the presence of urine and high -content ejaculation of leukocytes) and no inflammation in nature.
Reason
The cause of acute and chronic prostatitis is pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi).Usually, the source of inflammation is:
- E. coli;
- Streptococci;
- Staphylococci;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella;
- Fake bars;
- The pathogens of sexually transmitted diseases (Chlamydia, Mycoplasmas, Gonococci, Trichomonas, Cytomegalovirus and others).
Most microorganisms are in the intestines, on the skin, but, going into the tissue of the prostate, they cause an inflammatory process.As a rule, the cause of the disease is not a pathogen, but the relationship of some bacteria.
The development of chronic prostatitis can cause the following factors:
- Simultaneous diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- Little sedentary lifestyle ("sedentary work");
- Constipation trends;
- weakens the body's defense;
- injury;
- hormonal imbalance;
- Alcohol abuse and smoking;
- random sex;
- Abnormal sex life (long -term abstinence);
- interrupted sex;
- Irregular bladder drum;
- Sexual desire is not satisfied;
- chronic tension;
- Lower body temperature;
- The presence of tough teeth and other chronic sources of infections (for example, chronic tonsillitis).
Symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is a very cunning disease.It is difficult to catch that, because first, this process quickly becomes chronic and second, most patients like the manifestations of sinking of the acute prostatitis of the house.Patients with prostatitis are often sent to the doctor in advanced cases of erectile dysfunction and other consequences.
The acute form of the disease is based on the basis:
- fever;
- chills;
- Other signs of poisoning (weak, indifferent, loss of appetite, etc.).
Prostatitis is accompanied by pain in the perineum, in the groin area and in the scrotum.
Pain and fast urination are also characteristic.Sometimes in the urine, you may notice the discharge of white pus.
In addition, patients may pay attention to the lack of erection at night and in the morning, poor quality erections in the process of intimacy and shortening strong sex.
Typical symptoms of urination disorders appear: a weak urine stream and frequent urge, although urine stands out a bit.
In the future, in case of no treatment, chronic prostatitis to Apogei: sexual dysfunction appears.For example:
- not enough erection or absence;
- The erection is painful, so the patient avoids sex;
- Delete orgasm;
- Short intercourse;
- Sing of ejaculation.
Prostatitis becomes chronic 95% of all prostatitis, they are mostly about 30 years old.It is characterized by constant or pelvic pain in the pelvis, prostate, in the scrotum, while in the laboratory analysis there is no sign of inflammation.The causes of the disease are certainly not set.
Diagnose
In the diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis, in addition to collecting complaints, Anamnesis and patient examination, the following methods are used:
- Blood and urine tests in general;
- Check by microscopes of the secret of the prostate and sow it on the nutritional environment to detect pathogens (the secret obtained after massaging the prostate's fingers through the rectum);
- Cytological research of urine;
- Ultrasound of the prostate and pelvic organs;
- Computer layer and nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI);
- A stain from the urethra on the microbiological system.
Distinguished diagnosis for the purpose of distinguishing prostatitis, prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, signs of rock in prostate.
A full list of diagnostic procedures and drugs to treat prostatitis in federal support standards since 2012.
Treatment of prostatitis
Similar symptoms may be a sign of various diseases, and the disease may not occur according to textbooks.Do not try to treat yourself a doctor.An evolutionary surgeon leads to prostatitis.
The purpose of treating the cause to eliminate the cause of prostatitis is to eliminate pathogens.Depending on the cause, antibiotics, antiviral drugs or prescribed antifungal.The treatment time for acute prostatitis is 7-10 days, during chronic 4-8 weeks.
To treat bacterial infections, they are used:
- Antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- Macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- doxycycline;
- Antibacterial drugs.
Anti -fungal drugs (diflucan, fluconazole) are prescribed by oral and rectal candles.
In addition, other types of therapy are used:
- anti -allergic anti -allergic (Suprastin, Claritin, Dimedrol);
- Anti -inflammatory (indomethacin, diclofenac);
- Anesthesia (No-Shpa, Analgin, Baralgin).
They are also appointed:
- physiotherapy;
- Medical equipment;
- Prostate massage.
The whole treatment takes 3-4 months.
Prevent
To prevent disease, the following conditions must be observed:
- regular sex life;
- Refuse bad habits;
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle (playing sports, walking in fresh air);
- comply with diet;
- The visit regularly to the urinary doctor.